Difference Step-up and Down Transformer and Other Transformers
Step-up and Down Transformer play a vital role in today’s industrial power systems. Think of them as the “translators” of the electrical world, converting voltage levels so that every device gets the power it needs. Have you ever wondered why some transformers increase voltage while others decrease it? As a transformer manufacturer serving B2B clients, we understand how important Step-up and Down Transformer are in business procurement.
Choosing the right transformer not only ensures stable equipment operation but also directly affects production efficiency and energy costs. In this article, we’ll dive into the differences between step-up & step-down transformers and other types of transformers, helping you make informed decisions and select the best transformer for your business needs.
What Are Step-up and Down Transformer?
Definition
- Step-Up Transformer: A device that converts low voltage to high voltage.
- Step-Down Transformer: A device that converts high voltage to low voltage.
How They Work
The working principle of step-up and step-down transformers is based on electromagnetic induction. In simple terms, they consist of two or more windings (coils) wrapped around the same iron core. When alternating current flows through one winding (called the primary winding), it creates a magnetic field in the iron core. This magnetic field then induces a voltage in another winding (called the secondary winding). By adjusting the ratio of turns between the primary and secondary windings, the transformer can increase or decrease the voltage.
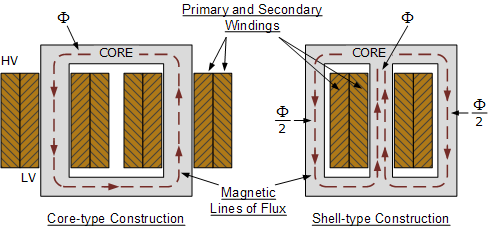
Typical Applications
- Step-Up Transformers: Commonly used in power transmission systems to increase the voltage generated by power plants, reducing energy loss during long-distance transmission.
- Step-Down Transformers: Widely used in factory distribution systems and household appliances to lower high voltage to safe levels required by equipment.
Structural and Operational Differences Between Step-up and Down Transformer
| Item | Step-Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Winding Turns | Secondary has more turns than primary | Primary has more turns than secondary |
| Voltage | Secondary voltage is higher | Secondary voltage is lower |
| Current | Secondary current is lower | Secondary current is higher |
| Application | Long-distance power transmission, high-voltage equipment | End-user devices, low-voltage applications |
| Notes | Higher insulation requirements to prevent breakdown | Must consider load capacity to avoid overload |
- Winding Ratio: The secondary winding of a step-up transformer has more turns than the primary, while the step-down transformer is the opposite.
- Voltage and Current Changes: When stepping up, voltage increases and current decreases; when stepping down, voltage decreases and current increases.
- Wire Thickness and Insulation: High-voltage windings often use thinner wires and require higher insulation.
- Energy Loss and Efficiency: Proper design reduces losses and improves transmission efficiency.
Comparing Step-up and Down Transformer With Other Common Types
The transformer family includes more than just step-up and down transformer types. Let’s meet some of the other key players:
- Autotransformer: Simple structure with only one winding, part of which acts as both primary and secondary.
- Isolation Transformer: Mainly used for electrical isolation to prevent electric shock and protect equipment.
- Special Transformers: Such as rectifier transformers and furnace transformers, designed for specific applications.
Just like specialists in different fields, each transformer type excels in its own area. So, how do you choose the right one for your business?
Common B2B Purchasing Needs and Pain Points for Step-up and Down Transformer
As a B2B client, you might face the following challenges when purchasing Step-up and Down Transformer:
- Custom Voltage Levels: Different equipment requires different voltage levels.
- Capacity Selection: Too small, and you risk overload; too large, and you waste resources.
- Reliability and Safety Standards: Safety comes first; stable operation is key.
- Energy Efficiency and Maintenance Costs: Over time, saving energy means saving money.
- Lead Time and After-Sales Service: Timely delivery and reliable support matter.
How to Choose the Right Step-Up or Down Transformer?
- Clarify Your Needs: Determine input voltage, output voltage, and load type.
- Calculate Capacity: Choose capacity based on equipment power, with some margin.
- Consider the Environment: Select the appropriate protection level for your setting.
- Check Standards: Ensure compliance with relevant national and industry standards.
- Choose a Trusted Brand: Work with manufacturers with a strong reputation and technical expertise.
If you have any questions during the selection process, feel free to contact us. We’re here to provide professional advice and custom solutions.
Why Choose Us as Your Transformer Partner?
- Experience and Technical Strength: We have years of experience and technical know-how in transformer manufacturing.
- Customer Case Studies: We’ve supplied quality transformers and services to many well-known companies.
- One-Stop Customization and After-Sales Commitment: From design to after-sales, we support you every step of the way.
By choosing us, you get:
- High-Quality Products: We strictly control every production step to ensure quality.
- Professional Technical Support: Our engineering team is always ready to assist you.
- Attentive After-Sales Service: Our comprehensive after-sales system gives you peace of mind.
Step-up and step-down transformers play a crucial role in B2B procurement. Choosing the right transformer ensures stable equipment operation, improves production efficiency, and reduces energy costs. As a professional transformer manufacturer, we are committed to providing high-quality, reliable products and expert solutions. If you have any transformer needs, please contact us—we’re ready to help! Interested in our products? Send us an inquiry or place your order, and we’ll arrange production and delivery as soon as possible.
FAQ
Can step-up and down transformer be interchanged?
Generally not recommended, as their design parameters differ.
What about transformer lifespan and maintenance?
Regular inspections, good ventilation, and avoiding overload are key.
Lead time and warranty service?
Depends on model and customization; we offer long-term warranty support.