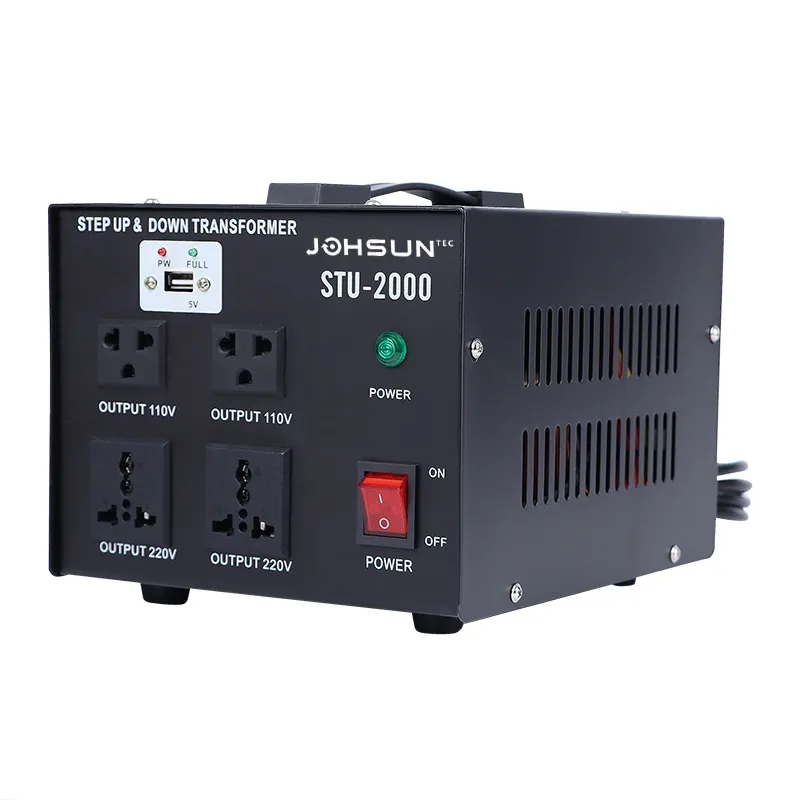
Structural Difference Between Step-Up and Down Transformer
In modern industrial and commercial sectors, the safety and efficiency of electrical equipment are critical priorities. Have you ever wondered how factory machinery operates so reliably? One unsung hero is the transformer—specifically, step-down transformers (Down Transformers) and step-up transformers. For B2B clients, choosing the right Step-Up and Down Transformer isn’t just about safety; it directly impacts operational costs and energy efficiency. This article dives into the structural and functional differences between these transformers, empowering you to make informed decisions. Need a tailored solution? Contact us today for expert guidance!
Basic Concepts of Transformers
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is a static electrical device that transfers energy between circuits via electromagnetic induction. Its core components are:
- Primary Winding: Connects to the power source.
- Secondary Winding: Delivers transformed voltage to the load.
- Core: Provides a low-resistance path for magnetic flux, enhancing efficiency.
How Do Transformers Work?
Transformers rely on mutual inductance. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field in the core, which induces voltage in the secondary winding. Voltage changes depend on the turns ratio:
Formula:
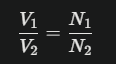
Where V1 and V2 are voltages, and N1 and N2 are winding turns.
Step-Down Transformer (Down Transformer): Structure and Operation
Definition and Applications
A Down Transformer converts high voltage to low voltage, ideal for:
- Factory power distribution
- Equipment protection
- Data centers
- Industrial automation
Structural Features
- Primary Winding: More turns (high voltage input).
- Secondary Winding: Fewer turns (low voltage output).
- Core: Laminated silicon steel cores with high permeability.
- Thicker Secondary Wire: Handles increased current after voltage reduction.
Working Principle
The primary winding receives high-voltage AC, while the secondary outputs low-voltage, high-current power.
Did You Know? Down Transformers not only reduce voltage but also boost current—critical for heavy-duty industrial machinery.
B2B Use Cases
- Factory power cabinets
- Industrial equipment power supply
- Server racks in data centers
- CNC machines and automated production lines
Struggling with voltage mismatches? Our Down Transformers offer seamless solutions!
Step-Up Transformer: Structure and Operation
Definition and Applications
Step-Up Transformers elevate low voltage to high voltage, used in:
- Long-distance power transmission
- Power plant outputs
- High-voltage industrial equipment
Structural Features
- Primary Winding: Fewer turns (low voltage input).
- Secondary Winding: More turns (high voltage output).
- Core: High-permeability silicon steel.
- Thinner Secondary Wire: Suitable for low-current, high-voltage output.
Working Principle
The primary winding draws low-voltage AC, while the secondary delivers high-voltage, low-current power.
Fun Fact: Why do power companies love step-up transformers? High-voltage transmission cuts energy losses, saving costs and reducing environmental impact!
B2B Use Cases
- Grid power transmission
- Power plant output systems
- High-voltage industrial devices
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Down Transformer | Step-Up Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Output Voltage | Lower than input | Higher than input |
| Turns Ratio | Primary > Secondary | Primary < Secondary |
| Output Current | Higher than input | Lower than input |
| Wire Thickness | Thicker secondary wire | Thinner secondary wire |
| Applications | Factories, equipment | Power transmission, high-voltage |
Key Takeaways
- Structural Differences: Turns ratio and wire thickness vary significantly.
- Functional Differences: Down Transformers lower voltage and raise current; Step-Up Transformers do the opposite.
- Selection Tip: Choose Down Transformers for factory equipment and Step-Up Transformers for power transmission.
While both Down Transformers and Step-Up Transformers are vital to power systems, their structural and operational differences dictate their roles. Down Transformers keep factories running safely, while Step-Up Transformers enable efficient energy transmission. At Johsun Tec, we specialize in high-performance Down Transformer and bespoke B2B solutions. Whether you’re a procurement manager or project engineer, our team is ready to optimize your power infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to Choose the Right Down Transformer?
Power Rating: Ensure it exceeds your equipment’s total demand.
Voltage Levels: Match input/output voltages to your needs.
Certifications: Opt for ISO/IEC-compliant products.
Environmental Factors: Check IP ratings and installation conditions.
What to Consider When Procuring Down Transformers?
Technical Expertise: Seek tailored solutions for your facility.
Delivery & Installation: Verify lead times and on-site support capabilities.
Maintenance Differences Between Step-Up and Down Transformers?
Testing: Perform oil analysis, insulation resistance tests, and thermal imaging.
Environment: Keep transformers dry, clean, and well-ventilated.
Don’t wait—reach out now and let Johsun Tec power your success!



